Japanese can be classified in various ways.Classification by Writing System
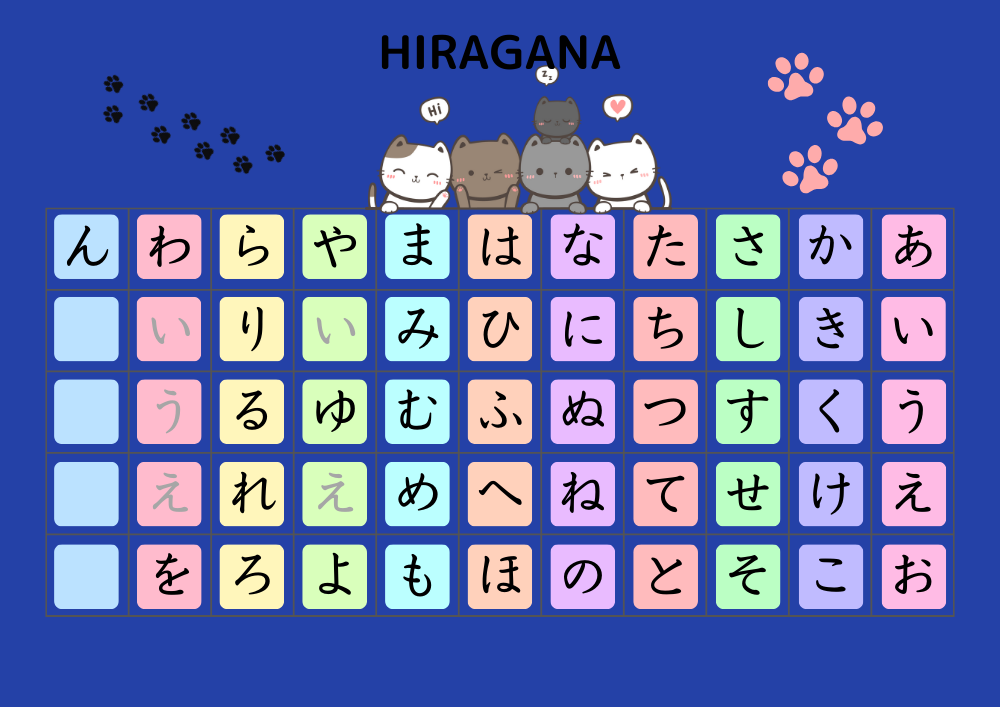
Hiragana (ひらがな):
The basic phonetic script of Japanese (e.g., ありがとう / arigatou – “thank you”).
Katakana (カタカナ):
Used for foreign loanwords and emphasis (e.g., コンピューター / konpyūtā – “computer”).
Kanji (漢字):
Chinese characters that carry meaning (e.g., 日本 – “Japan,” 東京 – “Tokyo,” 学生 – “student”)
Compared to English, Japanese has a basic set of 51 sounds. It is said that writing in the correct stroke order makes your handwriting look better, especially kanji.
1. Basic Sounds (Gojuon – 五十音図)
Japanese has a basic set of 50 sounds, but with the addition of “ん” (n), it becomes 51 sounds.
- Seion (清音 – “pure sounds”): Basic kana (あいうえお, etc.).
- “ん” (N – 撥音, Hatsuon): A nasal sound that is considered an independent syllable.
2. Sounds with Diacritics (Dakuten and Handakuten)
- Dakuten (濁音 – voiced sounds): Sounds with a diacritic (゛), such as ga, gi, gu, ge, go (がぎぐげご).
- Handakuten (半濁音 – semi-voiced sounds): Sounds with a small circle (゜), such as pa, pi, pu, pe, po (ぱぴぷぺぽ).
3. Contracted Sounds (Yōon – 拗音) and Small Kana
These are formed by combining kana with small “ゃ” (ya), “ゅ” (yu), “ょ” (yo), creating sounds like kya, shu, cho (きゃ, しゅ, ちょ, etc.).
4. Total Number of Sounds in Japanese
- Basic sounds: 51 (Gojuon + “ん”)
- Including voiced and semi-voiced sounds: About 70 sounds
- Including contracted sounds (yōon): Over 100 sounds
Maybe you can meet the new excitement in SHODOU!!


コメント